Angr符号执行
首先引用名言:
我超,这angr好几把神奇。 ——iPlayForSG
angr的安装
我在kali上用(EPsilon学长/姐)/iPlayForSG学长的方法没成功,最后用的这个
angr_find
这一关让我们来熟悉angr的用法

写出脚本:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| import angr
p = angr.Project('./00_angr_find')
init_state = p.factory.entry_state()
s = p.factory.simgr(init_state)
s.explore(find = 0x08048678)
if s.found:
print(s.found[0].posix.dumps(0))
else:
print("fail")
|
运行得出结果:
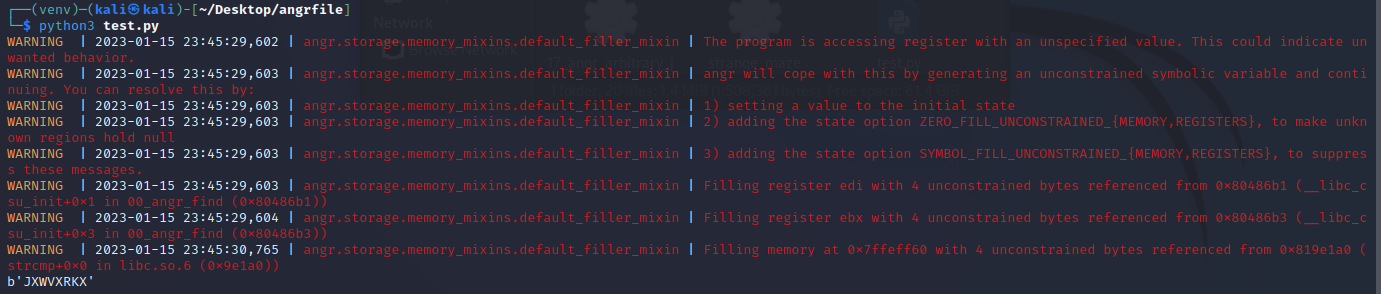
angr_avoid
这题的文件大小就预示着它很不一般,尤其是不要试图F5它的main()函数,会死机。
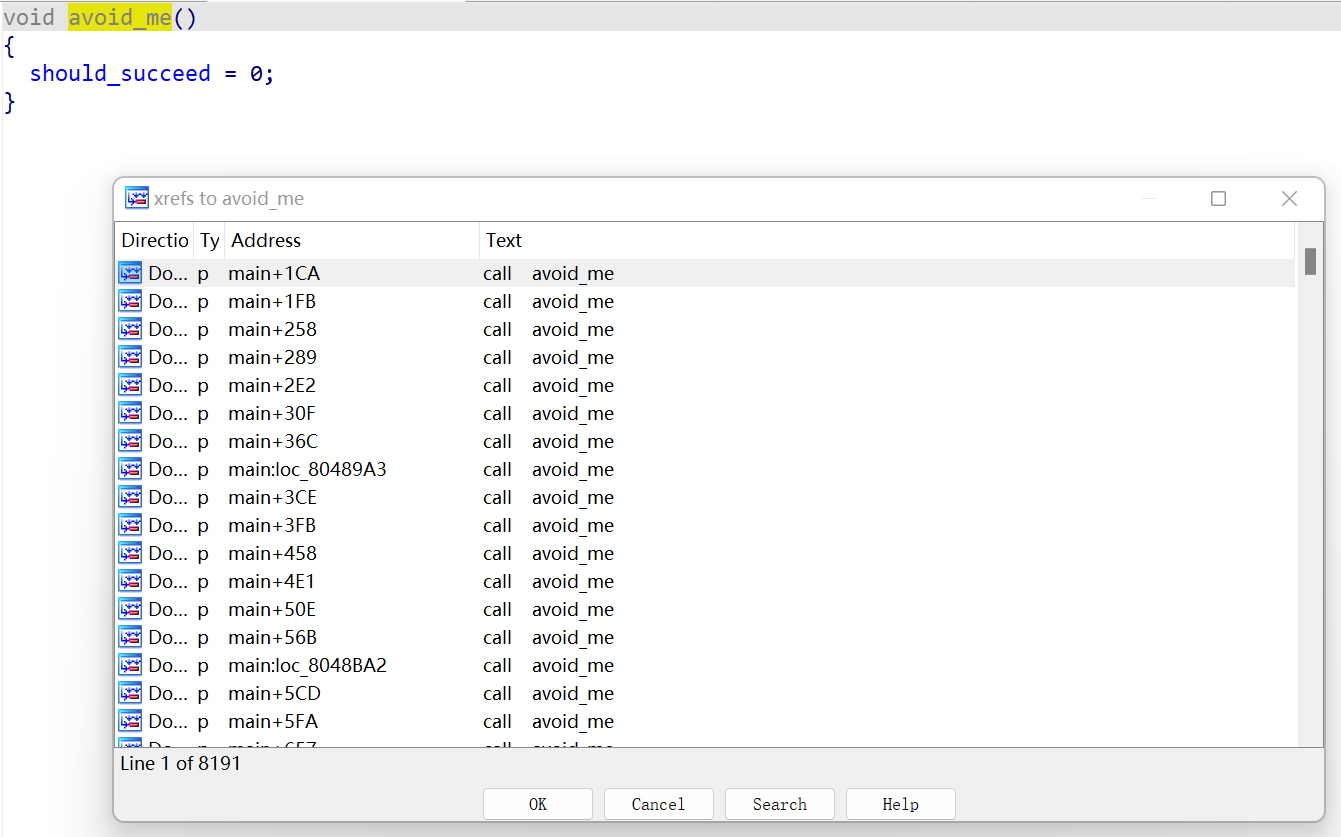
在maby_good()函数里看见有一个should_succeed:

查看交叉引用,发现它在avoid_me()函数中被赋0,而avoid_me()函数被调用了…8191次…
写出脚本
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| import angr
p = angr.Project('./01_angr_avoid')
init_state = p.factory.entry_state()
s = p.factory.simgr(init_state)
s.explore(find = 0x080485E0, avoid = 0x080485AB)
if s.found:
print(s.found[0].posix.dumps(0))
else:
print("fail")
|
运行得出结果
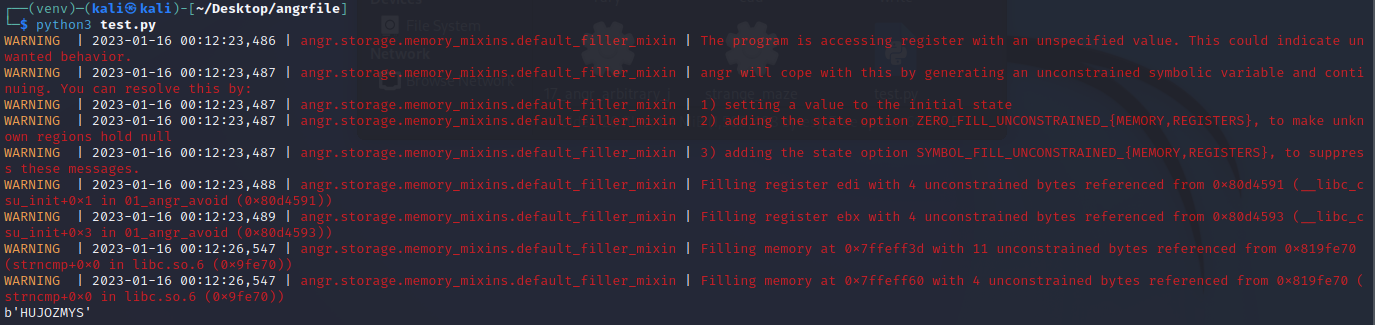
angr_find_condition
虽然主函数看起来人畜无害

但是左下角的graph view非常感人
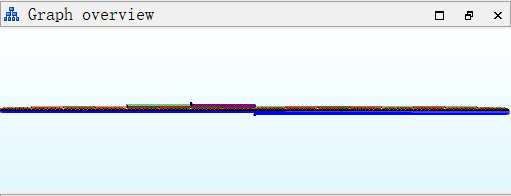
这个程序输出成功/失败提示的地方非常的多,用地址是不可能的了,所以检测输出
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| import angr
def aim_out(state):
return b'Good Job.' in state.posix.dumps(1)
def avoid_out(state):
return b'Try again.' in state.posix.dumps(1)
p = angr.Project('./02_angr_find_condition')
init_state = p.factory.entry_state()
s = p.factory.simgr(init_state)
s.explore(find = aim_out, avoid = avoid_out)
if s.found:
print(s.found[0].posix.dumps(0))
else:
print("fail")
|
运行得出结果
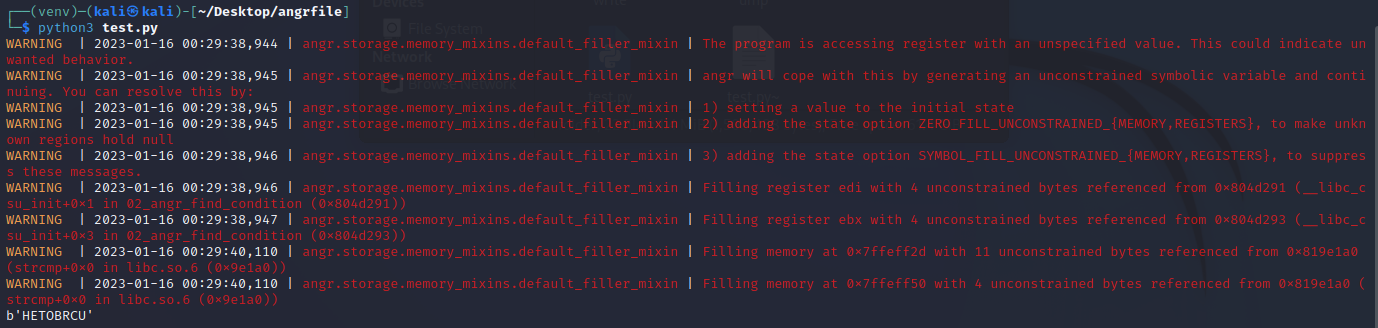
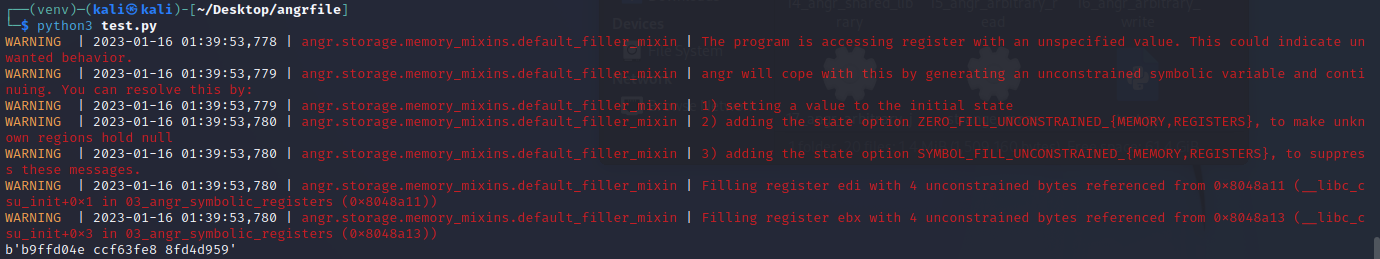
angr_symbolic_registers
题目描述说angr做不了三个输入的题,所以要人为构造输入,在IDA里找到三个位置分别是eax,ebx,edx
写出脚本
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| import angr
import claripy
def aim_out(state):
return b'Good Job.' in state.posix.dumps(1)
def avoid_out(state):
return b'Try again.' in state.posix.dumps(1)
p = angr.Project('./03_angr_symbolic_registers')
init_state = p.factory.entry_state()
s = p.factory.simgr(init_state)
s.explore(find = aim_out, avoid = avoid_out)
if s.found:
print(s.found[0].posix.dumps(0))
else:
print("fail")
|
为什么注释掉了一大堆捏?因为用推荐的方法写会报一大坨错,说数组越界,甚至用它给的标准答案都不行。angr在最初并不那么高级,但是现在高级了,也就不用这样了(然鹅理论上不应该报错才对)。运行得到结果
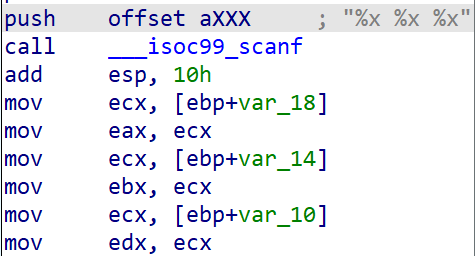
angr_symbolic_stack
同上一题,本意是在栈中手动模拟栈的操作,但是现在angr可以自己解决这个问题了。
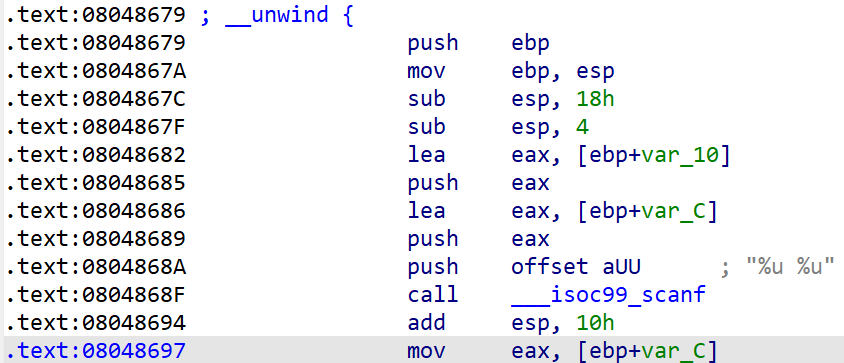
add esp, 10h是恢复栈的操作,因此我们从0x8048697开始程序,并手动将两个输入填充到占空间上
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| import angr
import claripy
def aim_out(state):
return b'Good Job.' in state.posix.dumps(1)
def avoid_out(state):
return b'Try again.' in state.posix.dumps(1)
p = angr.Project('./04_angr_symbolic_stack')
init_state = p.factory.blank_state(addr = 0x08048697)
init_state.regs.ebp = init_state.regs.esp
input0 = claripy.BVS('input0', 4 * 8)
input1 = claripy.BVS('input1', 4 * 8)
padding = 8
init_state.regs.esp -= 8
init_state.stack_push(input0)
init_state.stack_push(input1)
s = p.factory.simgr(init_state)
s.explore(find = aim_out, avoid = avoid_out)
if s.found:
print(('{:d} {:d}'.format(s.found[0].solver.eval(input0), s.found[0].solver.eval(input1))))
else:
print("fail")
|
具体原因如下

运行得到结果
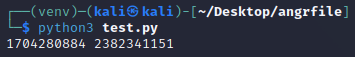
诶嘿,这个可以正常运行而且没有WARNING诶~
angr_symbolic_memory
这一题需要我们在.bss段创建输入,同样的,现在的angr已经不需要这么做了。
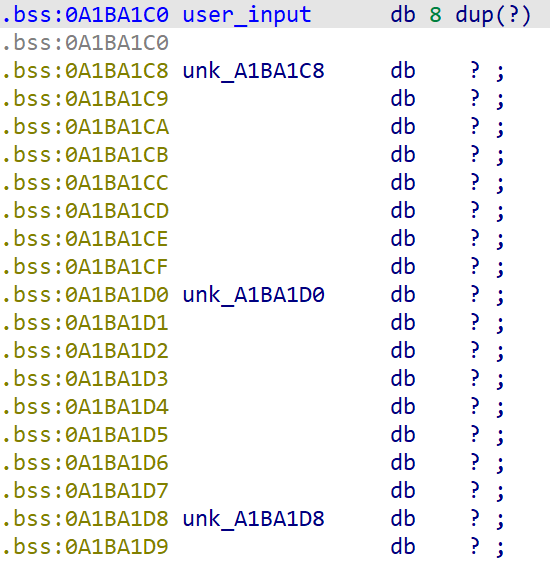
写出代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| import angr
import claripy
def aim_out(state):
return b'Good Job.' in state.posix.dumps(1)
def avoid_out(state):
return b'Try again.' in state.posix.dumps(1)
p = angr.Project('./05_angr_symbolic_memory')
init_state = p.factory.blank_state(addr = 0x08048601)
input0 = claripy.BVS('input0', 64)
input1 = claripy.BVS('input1', 64)
input2 = claripy.BVS('input2', 64)
input3 = claripy.BVS('input3', 64)
init_state.memory.store(0x0A1BA1C0, input0)
init_state.memory.store(0x0A1BA1C8, input1)
init_state.memory.store(0x0A1BA1D0, input2)
init_state.memory.store(0x0A1BA1D8, input3)
s = p.factory.simgr(init_state)
s.explore(find = aim_out, avoid = avoid_out)
if s.found:
print(('{} {} {} {}'.format(s.found[0].solver.eval(input0, cast_to = bytes), s.found[0].solver.eval(input1, cast_to = bytes), s.found[0].solver.eval(input2, cast_to = bytes), s.found[0].solver.eval(input3, cast_to = bytes))))
else:
print("fail")
|
运行得出结果
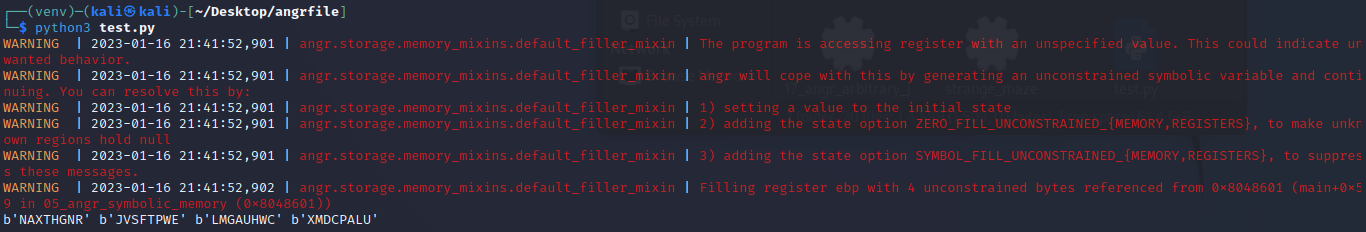
这次的运行速度和普通写法差不多,相比于前几题慢了一些
angr_symbolic_dynamic_memory
这一题需要我们在堆区写入输入
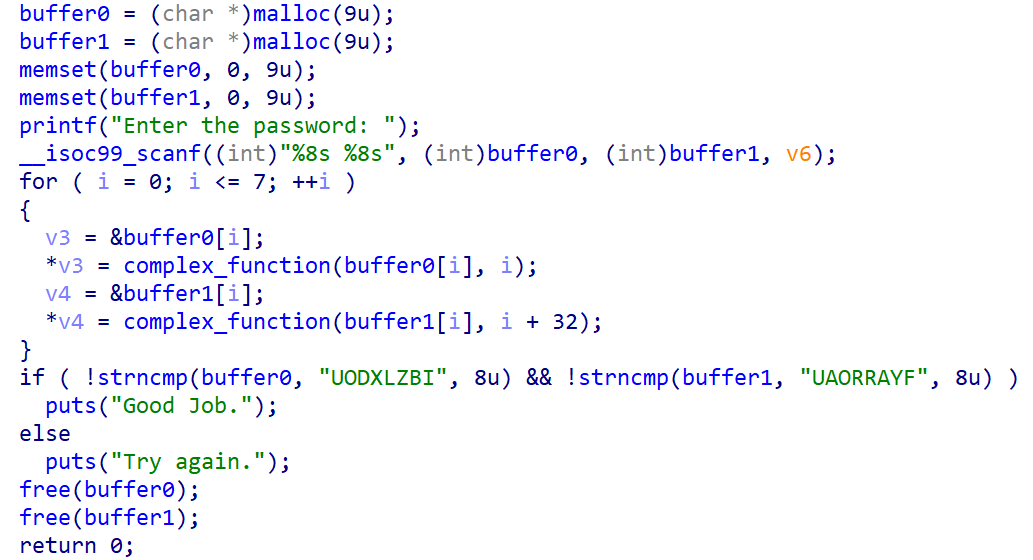
写出脚本
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| import angr
import claripy
def aim_out(state):
return b'Good Job.' in state.posix.dumps(1)
def avoid_out(state):
return b'Try again.' in state.posix.dumps(1)
p = angr.Project('./06_angr_symbolic_dynamic_memory')
init_state = p.factory.blank_state(addr = 0x08048699)
input0 = claripy.BVS('input0', 64)
input1 = claripy.BVS('input1', 64)
fake_heap0 = 0x0ABCC88F
fake_heap1 = 0x0ABCC859
addr_input0 = 0x0ABCC8A4
addr_input1 = 0x0ABCC8AC
init_state.memory.store(addr_input0, fake_heap0, endness = p.arch.memory_endness)
init_state.memory.store(addr_input1, fake_heap1, endness = p.arch.memory_endness)
init_state.memory.store(fake_heap0, input0)
init_state.memory.store(fake_heap1, input1)
s = p.factory.simgr(init_state)
s.explore(find = aim_out, avoid = avoid_out)
if s.found:
print(s.found[0].solver.eval(input0, cast_to = bytes) + b' ' + s.found[0].solver.eval(input1, cast_to = bytes))
else:
print("fail")
|
运行得出结果
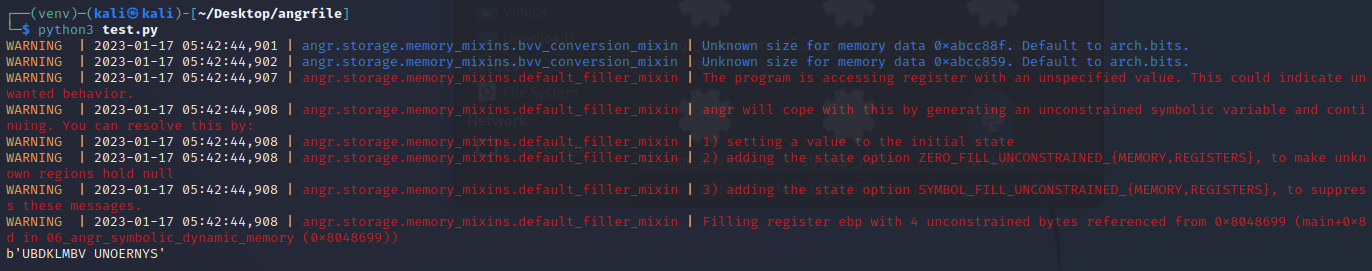
angr_symbolic_file
这题在文件中创建输入,从fopen前执行angr
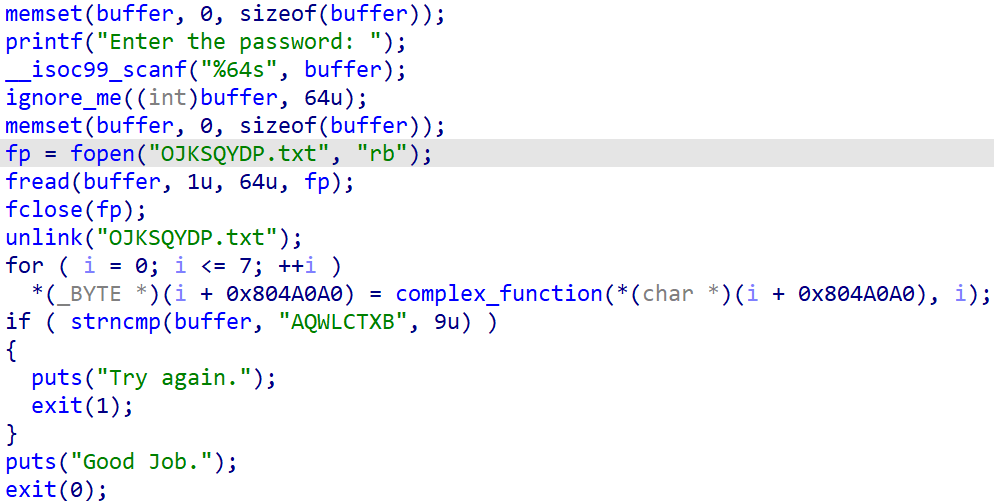
写出脚本
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| import angr
import claripy
def aim_out(state):
return b'Good Job.' in state.posix.dumps(1)
def avoid_out(state):
return b'Try again.' in state.posix.dumps(1)
p = angr.Project('./07_angr_symbolic_file')
init_state = p.factory.blank_state(addr = 0x080488EA)
filename = 'OJKSQYDP.txt'
file_size = 8
input = claripy.BVS('input', file_size * 8)
file = angr.SimFile(name = filename, content = input, size = 8)
init_state.fs.insert(filename, file)
s = p.factory.simgr(init_state)
s.explore(find = aim_out, avoid = avoid_out)
if s.found:
print(s.found[0].solver.eval(input, cast_to = bytes))
else:
print("fail")
|
运行得出结果
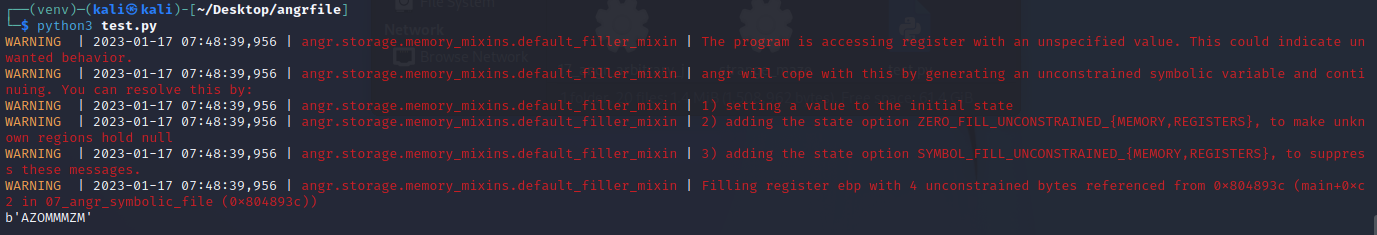
angr_constraints
这一题的对比函数会将16个字符判断完成后在进行反馈,这会导致angr的路径爆炸,因此我们需要在对比之前停下程序,自行对比
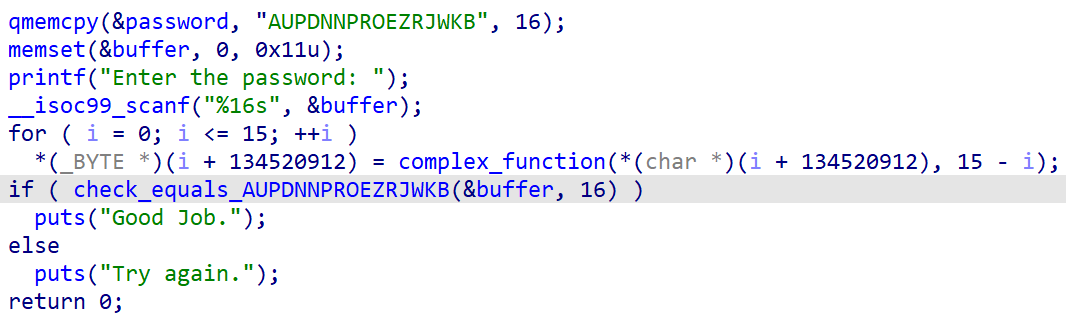
可以写出脚本
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| import angr
import claripy
p = angr.Project('./08_angr_constraints')
init_state = p.factory.blank_state(addr = 0x08048625)
input = claripy.BVS('input', 16 * 8)
init_state.memory.store(0x0804A050, input)
s = p.factory.simgr(init_state)
s.explore(find = 0x0804866C)
if s.found:
cmp_BVS = s.found[0].memory.load(0x0804A050, 16)
aim_BVS = b'AUPDNNPROEZRJWKB'
s.found[0].add_constraints(cmp_BVS == aim_BVS)
print(s.found[0].solver.eval(input, cast_to = bytes))
else:
print("fail")
|
现在angr高级了,在.bss存数据那一段用注释的内容也可以。运行得出结果
angr_hooks
本题中需要我们自行改写一个函数来避免路径爆炸
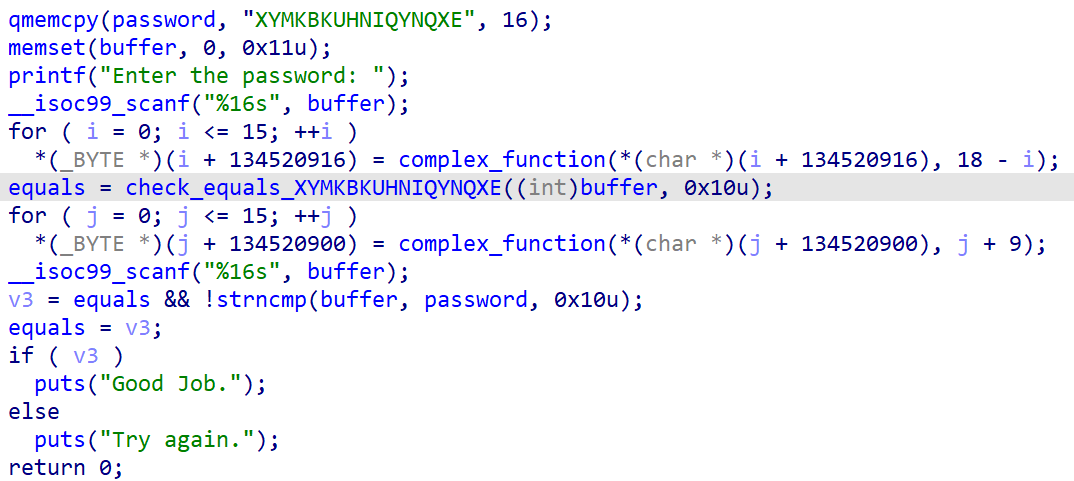
写出代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| import angr
import claripy
p = angr.Project('./09_angr_hooks')
init_state = p.factory.entry_state()
hook_addr = 0x080486B3
skip_length = 5
@p.hook(hook_addr, length = skip_length)
def my_check(state):
cmp_BVS = state.memory.load(0x0804A054, 16)
aim_BVS = b'XYMKBKUHNIQYNQXE'
state.regs.eax = claripy.If(cmp_BVS == aim_BVS, claripy.BVV(1, 32), claripy.BVV(0, 32))
s = p.factory.simgr(init_state)
def aim_out(state):
return b'Good Job.' in state.posix.dumps(1)
def avoid_out(state):
return b'Try again.' in state.posix.dumps(1)
s.explore(find = aim_out, avoid = avoid_out)
if s.found:
print(s.found[0].posix.dumps(0))
else:
print("fail")
|
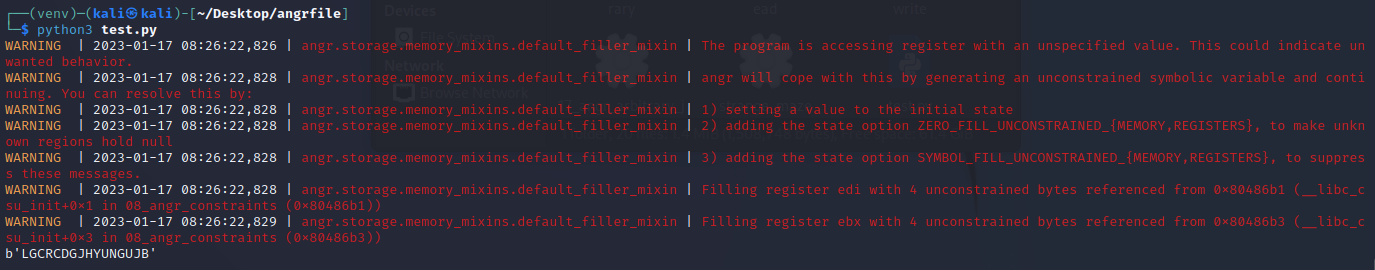
运行得出结果
angr_simprocedures
这一题还是hook函数,不过这个函数被调用了256次。因此我们决定hook函数本身而不是像上一题那样hook调用的指令
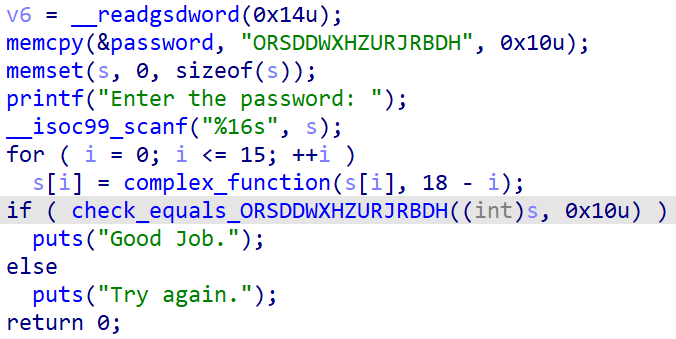
写出脚本
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| import angr
import claripy
p = angr.Project('./10_angr_simprocedures')
init_state = p.factory.entry_state()
class my_check(angr.SimProcedure):
def run(self, Str, len):
cmp_BVS = self.state.memory.load(Str, len)
aim_BVS = b'ORSDDWXHZURJRBDH'
return claripy.If(cmp_BVS == aim_BVS, claripy.BVV(1, 32), claripy.BVV(0, 32))
hook_func_addr = 0x080485F5
p.hook(hook_func_addr, my_check())
s = p.factory.simgr(init_state)
def aim_out(state):
return b'Good Job.' in state.posix.dumps(1)
def avoid_out(state):
return b'Try again.' in state.posix.dumps(1)
s.explore(find = aim_out, avoid = avoid_out)
if s.found:
print(s.found[0].posix.dumps(0))
else:
print("fail")
|
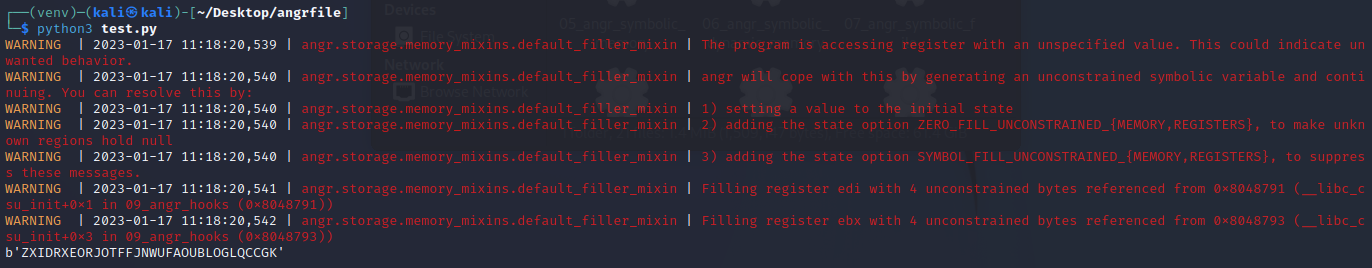
运行得出结果
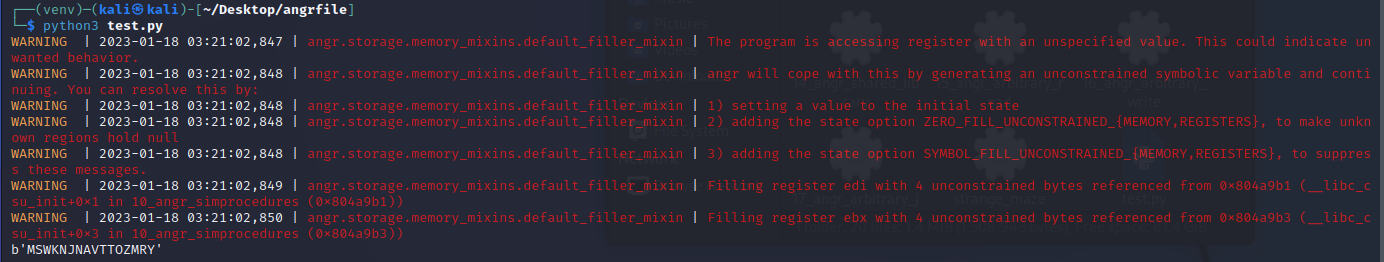
angr_sim_scanf
这一题的scanf()函数被调用了256次,由于古老版本angr处理不了多参数输入,因此需要hook,但现在angr已经不需要了
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| import angr
import claripy
p = angr.Project('./11_angr_sim_scanf')
init_state = p.factory.entry_state()
class my_scanf(angr.SimProcedure):
def run(self, format_string, input_addr0, input_addr1):
input0 = claripy.BVS('input0', 32)
input1 = claripy.BVS('input1', 32)
self.state.memory.store(input_addr0, input0, endness = p.arch.memory_endness)
self.state.memory.store(input_addr1, input1, endness = p.arch.memory_endness)
self.state.globals['input0'] = input0
self.state.globals['input1'] = input1
p.hook_symbol('__isoc99_scanf', my_scanf())
s = p.factory.simgr(init_state)
def aim_out(state):
return b'Good Job.' in state.posix.dumps(1)
def avoid_out(state):
return b'Try again.' in state.posix.dumps(1)
s.explore(find = aim_out, avoid = avoid_out)
if s.found:
print(s.found[0].solver.eval(s.found[0].globals['input0']), s.found[0].solver.eval(s.found[0].globals['input1']))
else:
print("fail")
|
运行得出结果
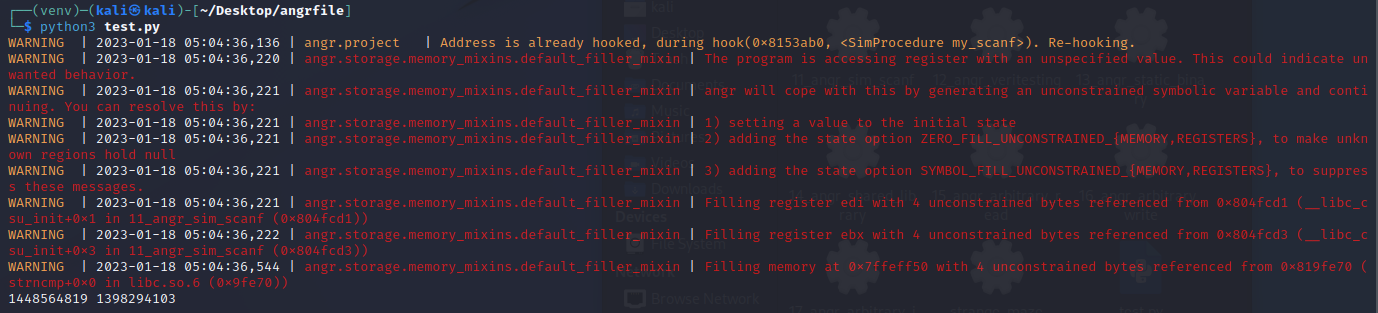
angr_veritesting
Angr越来越高级了,现在我们只需要半行代码就可以自动规避一些路径爆炸了
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| import angr
p = angr.Project('./12_angr_veritesting')
init_state = p.factory.entry_state()
s = p.factory.simgr(init_state, veritesting = True)
def aim_out(state):
return b'Good Job.' in state.posix.dumps(1)
def avoid_out(state):
return b'Try again.' in state.posix.dumps(1)
s.explore(find = aim_out, avoid = avoid_out)
if s.found:
print(s.found[0].posix.dumps(0))
else:
print("fail")
|
运行得出结果
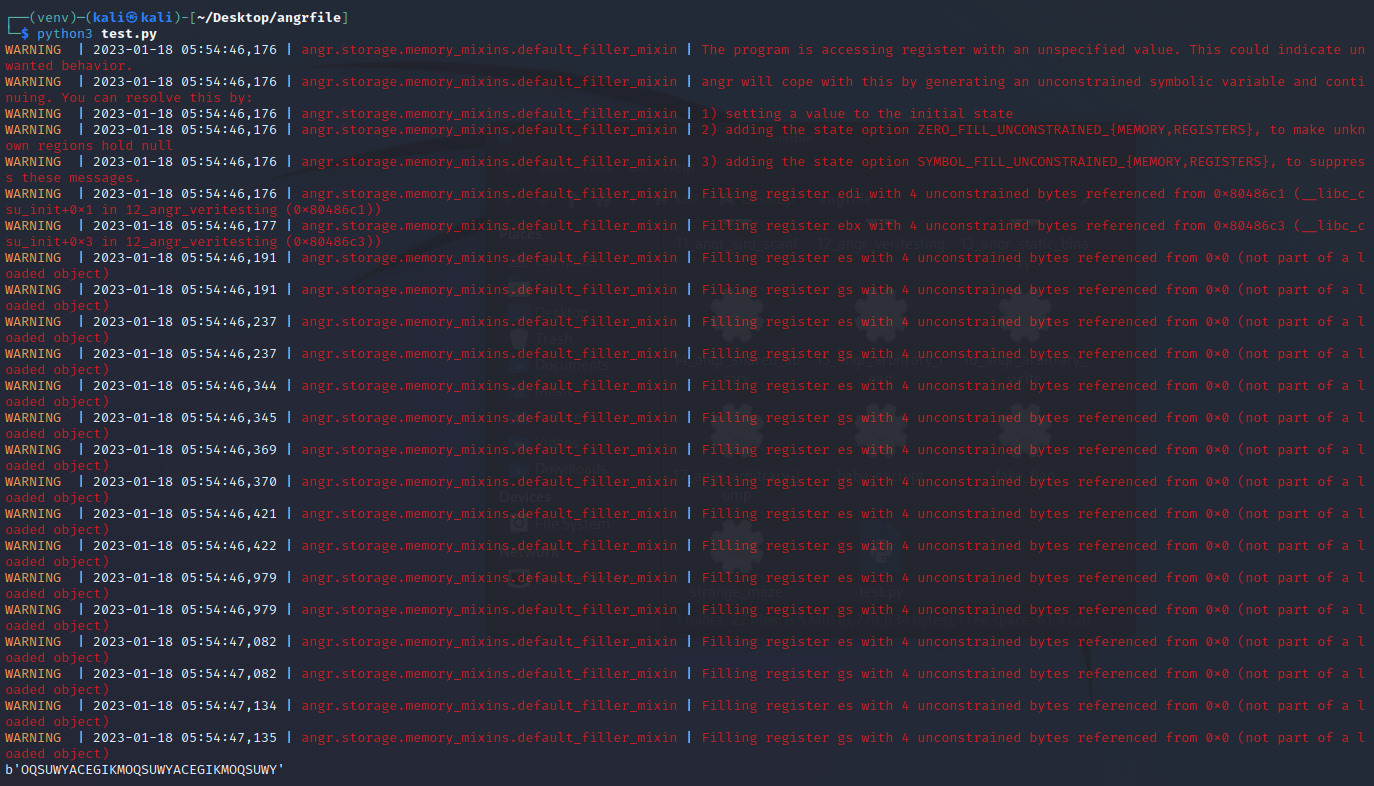
angr_static_binary
这一题的程序采用静态编译。angr在模拟动态编译的程序时会将系统函数替换成自己的一套更快的代码。然而对于静态编译的程序则需要我们自己手动hook。好在angr提供了他自己的那一套代码。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| import angr
p = angr.Project('./13_angr_static_binary')
init_state = p.factory.entry_state()
s = p.factory.simgr(init_state, veritesting = True)
p.hook_symbol('__libc_start_main', angr.SIM_PROCEDURES['glibc']['__libc_start_main']())
p.hook_symbol('printf', angr.SIM_PROCEDURES['libc']['printf']())
p.hook_symbol('__isoc99_scanf', angr.SIM_PROCEDURES['libc']['scanf']())
p.hook_symbol('puts', angr.SIM_PROCEDURES['libc']['puts']())
p.hook_symbol('_strcmp', angr.SIM_PROCEDURES['libc']['strcmp']())
def aim_out(state):
return b'Good Job.' in state.posix.dumps(1)
def avoid_out(state):
return b'Try again.' in state.posix.dumps(1)
s.explore(find = aim_out, avoid = avoid_out)
if s.found:
print(s.found[0].posix.dumps(0))
else:
print("fail").posix.dumps(0))
else:
print("fail")
|
运行得出结果(WARNING太多了,截不全)
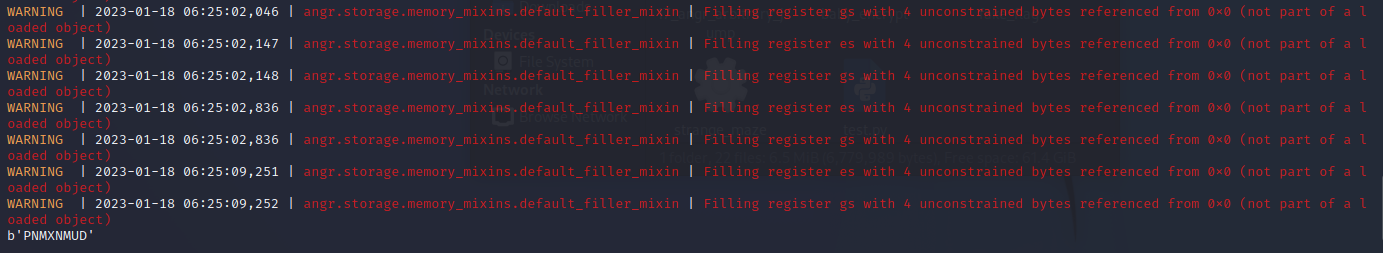
结束语
再次引用名言:
我超,这angr好几把神奇。 ——iPlayForSG





























![[TSCTF-J2024]二进制漏洞题解](/img/%5BTSCTF-J2024%5D%E4%BA%8C%E8%BF%9B%E5%88%B6%E6%BC%8F%E6%B4%9E%E9%A2%98%E8%A7%A3/cover.jpg)


